The Fascinating World of Amphibian Skin
Ever wondered about the unique skincare routine of amphibians? Unlike their reptilian cousins, amphibians have a fascinating approach to maintaining and utilizing their skin that’s unlike any other in the animal kingdom. Let's dive into how these creatures shed their skin and why it really matters to them.
Unveiling the Unique Skin of Amphibians
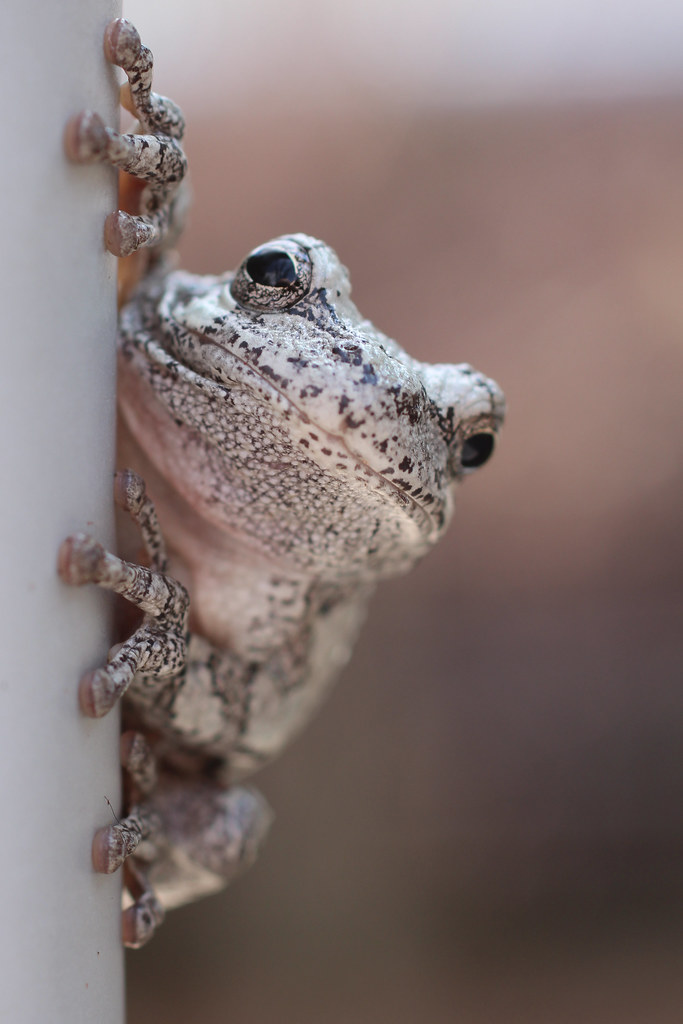

Amphibians are famous for their soft, moist skin, which plays multiple critical roles in their survival. While some, like toads, have thicker, drier skin, others such as mudpuppies are notably slimy. This moisture is not just for appearance's sake; it’s essential for their ability to breathe and hydrate. Yes, that's right—they can breathe and absorb water directly through their skin! For a deeper understanding of their classification and unique characteristics, you can explore more about amphibians on this Wikipedia page.
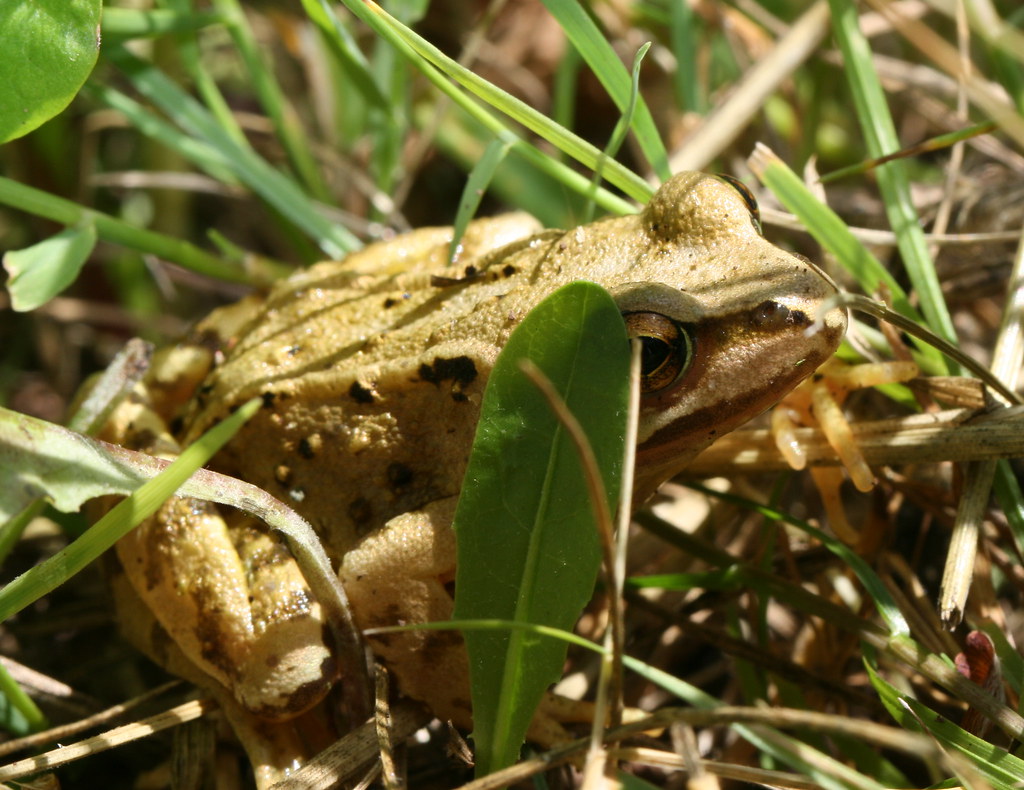

The Shedding Process Explained
Distinct from reptiles, who leave their shed skin behind, amphibians have a rather unique approach. They shed their outer skin several times a year, and here's the twist—they consume the shed skin. This behavior might seem odd, but it’s packed with purpose. Eating their shed skin allows them to recycle nutrients and maintain a clean environment, as leaving it behind could attract parasites or predators.
Why Shedding Matters
Shedding is not just about getting rid of old skin; it’s about survival. Amphibians' skin is their first line of defense. Some even possess bad-tasting chemicals in their skin, which can deter predators. This natural defense, combined with the ability to blend into their environment through unique coloration and sometimes even color change, makes their skin a vital tool in avoiding threats.
How Amphibians Compare to Other Animals
| Animal Type | Shed Skin | Skin Functionality |
|---|---|---|
| Amphibians | Shed and consume | Gas exchange, water absorption, defense |
| Reptiles | Shed, not consumed | Protection, thermoregulation |
| Mammals | Not applicable | Protection, thermoregulation |
Each type of animal has evolved distinct methods of utilizing their skin tailored to their lifestyle and environment.
The Adaptive Advantage of Amphibian Shedding
Amphibians' ability to shed skin and then consume it gives them an adaptive edge. By avoiding waste and recycling nutrients, they maintain a balanced diet if food is scarce. Additionally, regularly shedding their skin helps with pest control, preventing a buildup of harmful bacteria or parasites.
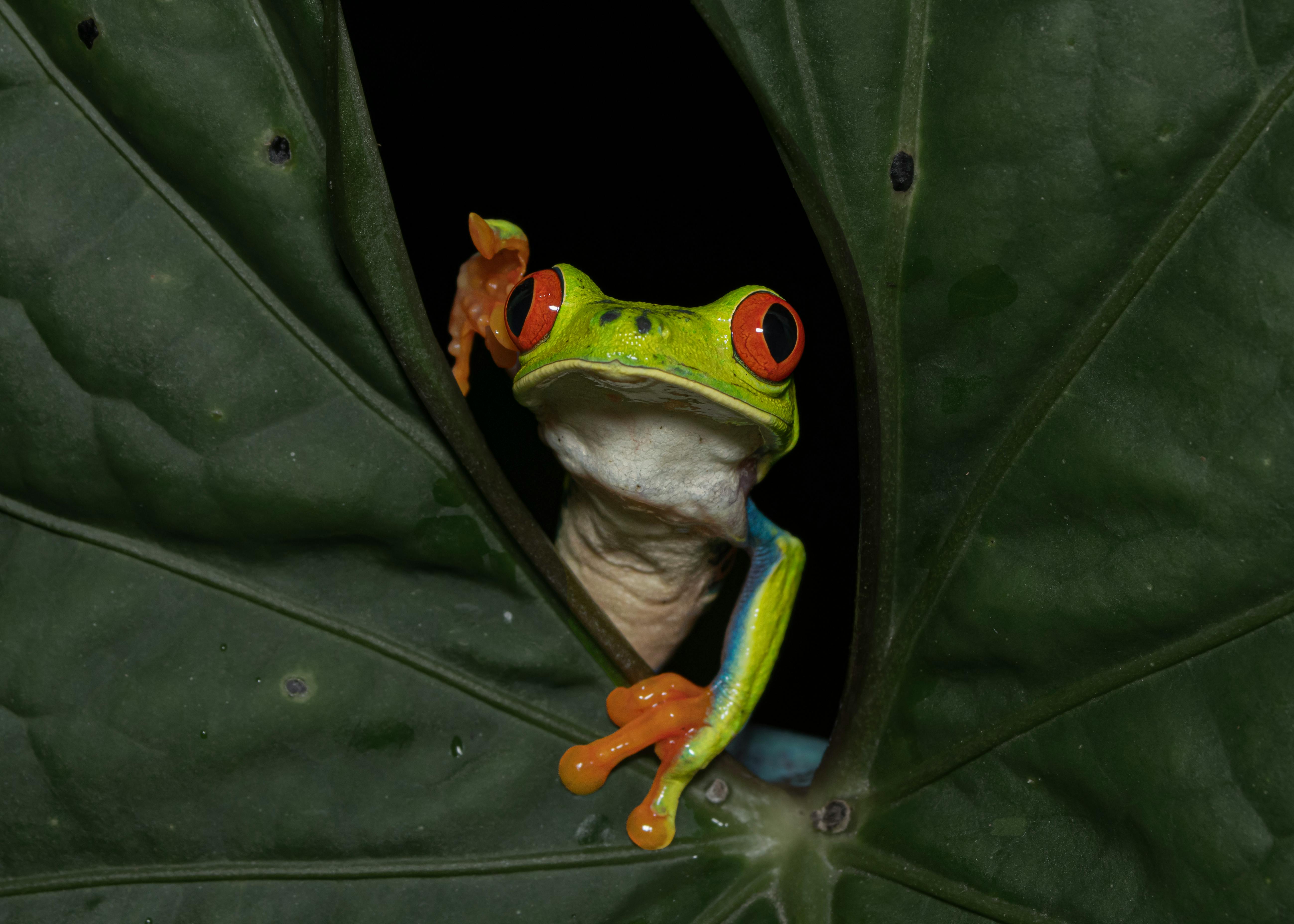

So, the next time you see a frog leaping by or a salamander basking on a wet rock, remember the incredible utility of their skin and the compelling reasons behind their ‘skincare’ rituals. These ancient creatures have developed a skin-care system that’s environmentally mindful and perfectly adapted to their needs.
What do you think about this unique process? Have you ever seen an amphibian shedding its skin or consuming it? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below!
Frequently Asked Questions
Do all amphibians shed their skin?
Yes, all amphibians shed their skin. Shedding is essential for their survival as it allows them to maintain healthy skin that absorbs water and oxygen. If their skin becomes dry or damaged, it can harm these critical functions and affect their overall health.
How often do amphibians shed their skin?
The frequency of shedding varies among amphibians. Some may shed their skin as often as daily, while others may shed every few weeks. Regular shedding ensures their outer skin layer remains functional and healthy.
Why do amphibians eat their shed skin?
Amphibians often eat their shed skin to recycle nutrients and avoid leaving traces that might attract predators. This behavior is both a survival strategy and an efficient way to conserve resources.
What happens if an amphibian's skin is damaged?
If an amphibian's skin is damaged or dries out, it may struggle to absorb water and oxygen effectively. This can lead to health problems or even put its life at risk, which is why regular shedding is crucial for amphibian well-being.
How long does it take for amphibians to shed their skin?
The process of shedding skin in amphibians is typically quick, often completed within minutes. The exact duration depends on the species and environmental conditions.
As we wrap up our exploration into the peculiar habits of amphibians and their transformative skincare routine, remember that the wonders of nature are just a click away. If you're as captivated by these slippery skinned creatures as we are, why not stay connected and discover more fascinating stories and behind-the-scenes content? Follow us on Pinterest to pin more curious wildlife insights to your collection, or head over to Instagram for a visual feast of amazing amphibians and other unique natural wonders. Quick updates and lively conversations are always happening on our X (formerly Twitter) channel, and don't miss out on joining our community on Facebook for tips and exchanges of wild stories. We love hearing from fellow nature enthusiasts, so come say hi and let's dive deeper into this magical world together!
